The department was established on September 1, 1986 and consists of the laboratory of plasma-chemical processes, group of organizational and technical support and group of composite materials, which include 1 Doctor of Sciences and 2 PhDs.
The experimental results were published in more than 300 publications, including 1 monograph, 20 patents and 3 theses. Click here to see a more detailed list.
Main directions of activity:
- investigation of the gas-phase crystallization of metals, alloys and compounds on their basis by thermal and plasma-chemical reduction of metal-containing compounds;
- production of corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant and heat-resistant coatings for engineering, chemical industry, rocketry, electronics, medicine;
- manufacture of the products in the form of crucibles, pipelines, pressure vessels, thermal elements, equipment for high-temperature vacuum furnaces.
Major achievements:
The kinetics of phase redistribution in the MoSi2-W system at 1500 - 1800°С was studied. The kinetic parameters for the growth of lower silicides (Mo,W)5Si3 and the decrease in the layer of higher silicide MoSi2 depending on the oxidation temperature were determined. It was found that the stability of the MoSi2-W system exceeds the stability of the MoSi2-Mo and WSi2-W.
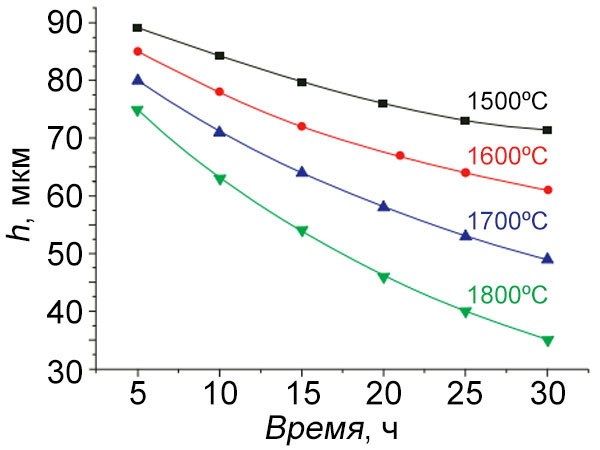
Dependence of MoSi2 decomposition rate on heating time
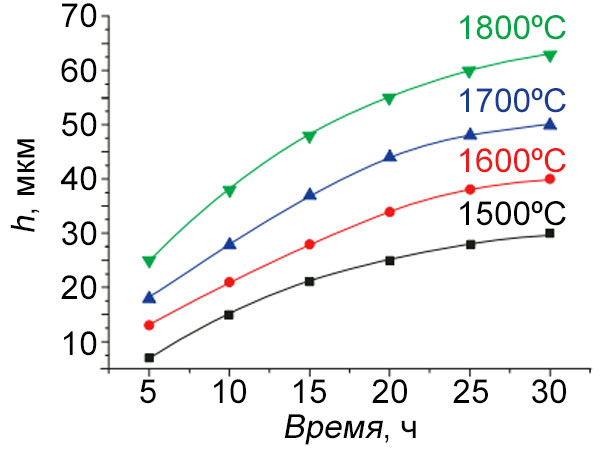
Dependence of (Mo,W)5Si3 phase growth rate on heating time
The influence of alloying additions of rhenium on the strength characteristics of tungsten-rhenium alloys was studied. It is shown that additions of rhenium injected into tungsten during co-deposition from the gas phase of their fluorides lead to the increase in bending strength from ∼ 340 MPa for tungsten to ∼ 800 MPa for tungsten-rhenium alloys with the rhenium content of ∼ 11 wt.%. In this case, the brittle-plastic transition temperature Тх is decreased from 600 to ∼ 200°С.
| Condensate composition | Measured value | Tdep = 450°C | Tdep = 550°C | Tdep = 650°C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cylindrical substrate | Flat-surface substrate | Cylindrical substrate | Flat-surface substrate | Cylindrical substrate | Flat-surface substrate | ||
| W | σprod, MPa | 340 | 415 | 365 | 330 | 415 | 380 |
| W + 3% Re | 280 | 805 | 785 | 750 | 770 | 815 | |
| W + 11% Re | 775 | 920 | 850 | 825 | 885 | 740 | |
| W | Tx, °C | 580 | 685 | 630 | 570 | 550 | 640 |
| W + 3% Re | 225 | 240 | 245 | 235 | 210 | 255 | |
| W + 11% Re | 180 | 200 | 220 | 175 | 205 | 215 | |
The barrier tightly adherent coatings based on refractory metals and applied in accordance with the developed technologies on the Zr or V cladding of fuel elements are obtained. The coatings provide their protection from the impact of nuclear fuel based on uranium carbides or uranium metal and increase their reliability.
| Material | Sublayer thickness, μm | Average bond strength, MPa |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| substrate | coating | ||
| Zr* | Mo-W | — | 0.2 |
| V* | Mo-W | — | 0.3 |
| Zr** | Mo-W | — | 5 |
| V** | Mo-W | — | 6 |
| Zr | Mo-W | 2 | 10 |
| V | Mo-W | 2 | 12 |
| Zr | Mo-W | 6 | 20 |
| V | Mo-W | 6 | 22 |
| Zr | Mo-W | 10 | 82 |
| V | Mo-W-Cr | 10 | 86 |
| Zr | Mo-W | 10 | 90 |
| V | Mo-W-Cr | 10 | 86 |
Strength characteristics of uranium dioxide particles coated with chromium, vanadium, Al2O3-Cr and Al2O3-V alloy in the temperature range of
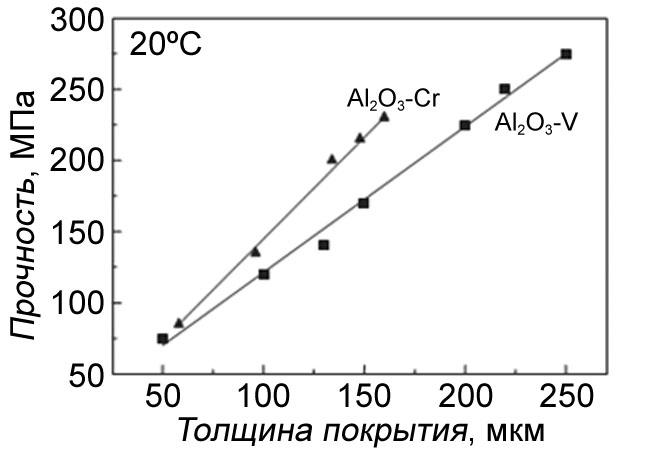
Compressive strength versus coating thickness for coated particles
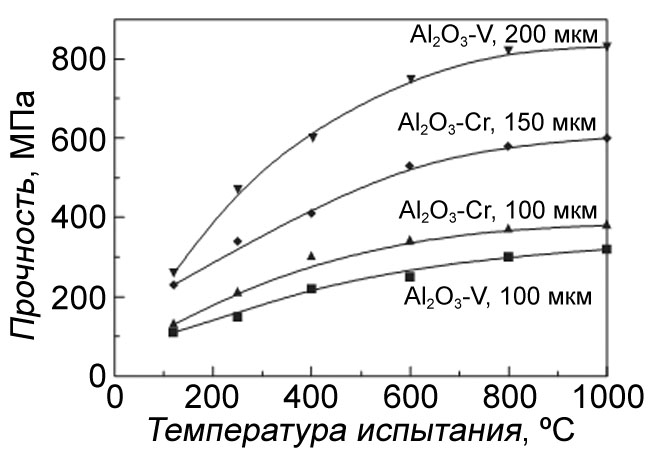
Temperature effect on particle strength
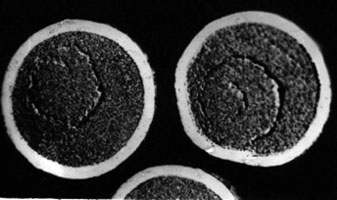
Original particles
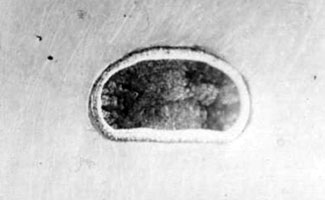
Deformed particles
The research on obtaining a cavitation-resistant coating based on boron carbide was carried out using hydrogen reduction of boron trichloride BCl3 and toluene C7H8. The experimental results on determining the magnitude of erosion damage show that the specimen with the boron carbide based coating undergoes 2.5 times less cavitation wear than austenitic steel.
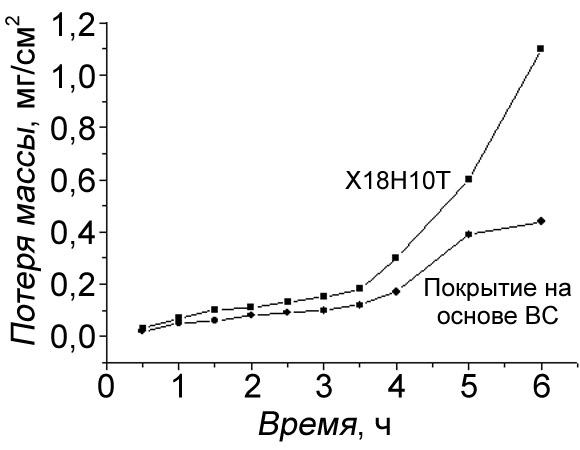
Erosional destruction

Sublimation source
The source of Si-Ge-B and Si-Ge-P atoms on Mo and W substrates for sublimation deposition of Si1-x-Gex(0.01 ≤ x ≤ 0.05) doped with B and P was obtained for the first time using the gas-phase method. The source allows expanding the range of applied substances, ranges of operating temperatures for evaporation and vapor pressures of Si-Ge-B and Si-Ge-P, which significantly improves the operational properties and deposition effectiveness.
It is shown that the obtained multilayer heteroepitaxial structure on the single-crystal Si and Si0.97-Ge0.03:B(∼ 1018 cm−3) substrates with the Si0.95-Ge0.05:B(∼ 1018 cm−3) buffer layer and Si0.95-Ge0.05:B(1017 - 1018 cm−3) and Si0.99-Ge0.01:B(∼ 1018 cm−3) upper epitaxial layers are characterized by photo-EMF and photosensitivity in the near-IR radiation region at the wavelength of ∼ 0.8 - 1 μm, which is important for further development of optoelectronic devices.
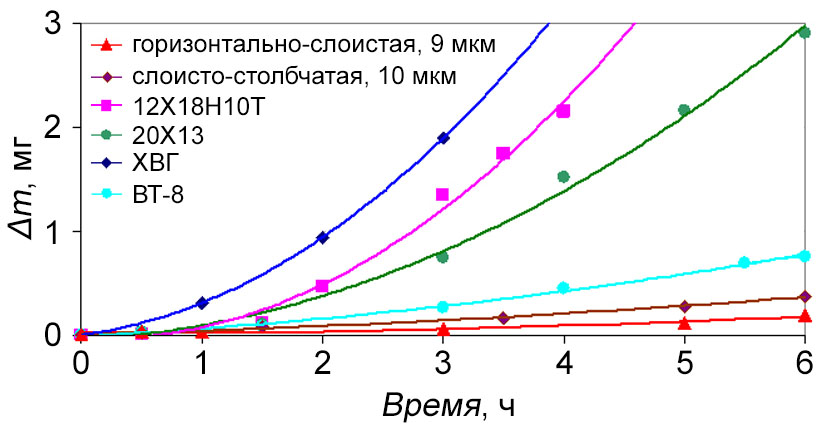
The structure and composition of the carbide-chromium coatings obtained from the OCL "Barhos", as well as their corrosion and erosion resistance, depending on the deposition process parameters, were studied. For the first time, the formation of two-level layered structure of carbide-chromium coating and the effect of reducing the surface roughness for the products after coating deposition from Ra = 0.7 - 1.2 μm to Ra = 0.4 - 0.6 μm were revealed. It is found that the increased coating resistance can be explained by the nano-size of coating structural elements and their layered structure, and the maximum values of adhesion, corrosion and erosion resistance are achieved at the deposition temperatures of 500 - 550°С.
Cavitation wear
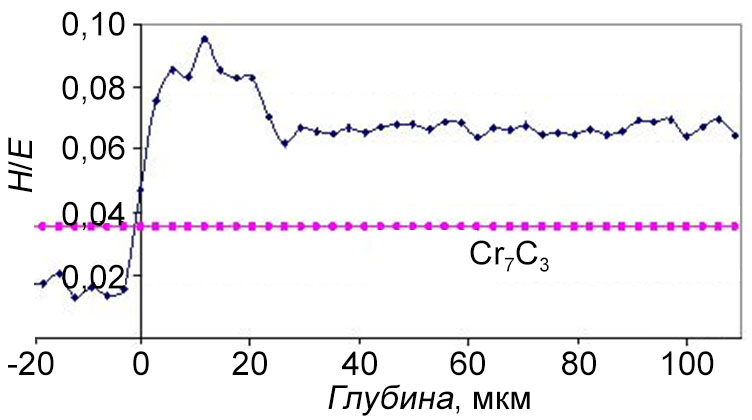
Wear resistance
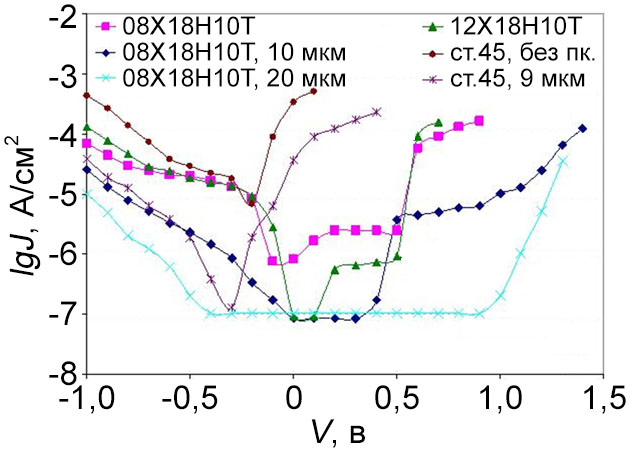
Comparative electrochemical characteristics
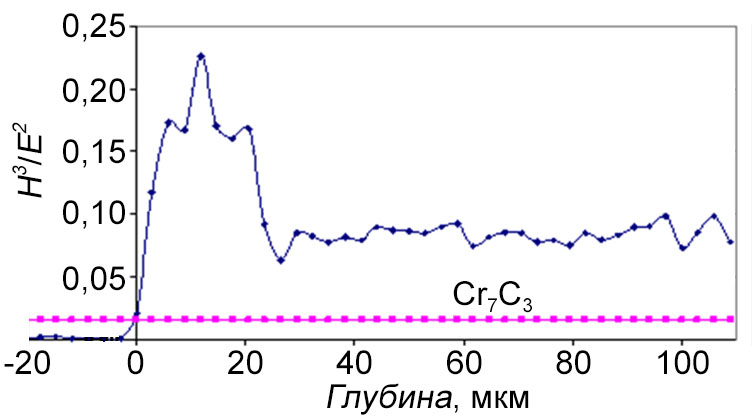
Plastic deformation resistance
Department structure
- The laboratory of plasma-chemical processes.
- The group of gas-phase and plasma-chemical deposition of materials.
Currently, the main activities of the laboratory are: gas-phase and plasma-chemical reduction of monosilane and silicon tetrachloride; production of doped silicon films; study of the condensate properties; production of cavitation-resistant coatings on the bends of switching pipelines for steam generators; development of the deposition process for the textured tungsten coatings on the cathodes for device engineering.
Publications
| 1. | П.И. Глушко, А.Ю. Журавлев, Н.А. Семенов, Н.А. Хованский, Б.М. Широков, А.В. Шиян, В.В. Щербакова. Исследование кинетики образования фаз в системе MoSi2-W в условиях нагрева при температурах 1500 - 1800°С. Физическая инженерия поверхности. 2014, т. 12, №2, с. 219 - 222. |
|---|---|
| 2. | А.Д. Осипов. О зависимостях характеристик распределения примесей у некоторых систем, содержащих элементы IV-VI групп. Вестник Национального технического университета «Харьковский политехнический институт». 2014, №28, с. 98 - 102. |
| 3. | А.Д. Осипов. О зависимостях температур изменения напряжений течения у некоторых элементов IV группы и других характеристик. Вестник Национального технического университета «Харьковский политехнический институт». 2014, №53, с. 179 - 184. |
| 4. | А.Д. Осипов. О зависимостях энтальпий образования у некоторых материалов, содержащих элементы IV–VII группы и других характеристик. Вестник Национального технического университета «Харьковский политехнический институт». 2014, №27, с. 148 - 152. |
| 5. | С.А. Крохмаль, Т.Н. Зуева. Получение карбидохромовых покрытий на изделиях сложного профиля и исследование защитных свойств материала покрытия. Физическая инженерия поверхности. 2014, т. 12, №2, с. 269 - 278. |
| 6. | А.Ю. Журавлев, А.В. Шиян, Н.А. Семенов, В.В. Левенец, Б.М. Широков, Г.В. Бокучава, Г.Ш. Дарсавелидзе. Сублимация Si-Ge из силицидогерманидов тугоплавких металлов. Georgia Chemical Journal. №14(1), с. 70 - 72. |
| 7. | А.Д. Осипов. О зависимостях характеристик поверхностной энергии у некоторых материалов, содержащих элементы IV-VI групп. Вестник Национального технического университета «Харьковский политехнический институт». 2014, №53, с. 173 - 178. |
| 8. | А.Н. Дериземля, П.Г. Крышталь, В.И. Радченко, Д.А. Хижняк, Б.М. Широков, А.И. Евсюков. Расчёт генератора для возбуждения индукционного разряда. Вестник Национального технического университета «Харьковский политехнический институт». |
| 9. | А.Д. Осипов. Применение эффективных потенциалов для определения температур изменения напряжений течения, плавления у некоторых элементов III-VI группы и других характеристик. УФЖ. |
| 10. | П.И. Глушко, А.Ю. Журавлев, Н.А. Хованский, Б.М. Широков, А.В. Шиян. Осаждение W и WRe сплавов газофазным и плазмохимическим методами. Вопросы Атомной Науки и Техники. Серия «Вакуум, чистые материалы, сверхпроводники». 2016, №1(101), с. 108 - 111. |
| 11. | С.А. Крохмаль, Б.М. Широков, Т.Н. Зуева, Н.А. Семенов. Структурные особенности карбидохромовых покрытий, получаемых методом MOCVD из ХОЖ «Бархос». Сборник научных статей по результатам, полученным в 2013 - 2015 по программе «Ресурс». |
| 12. | С.А. Крохмаль, Б.М. Широков, Т.Н. Зуева. Физико-химические свойства карбидохромовых покрытий, полученных методами MOCVD из ХОЖ «Бархос». Сборник научных статей по результатам, полученным в 2013 - 2015 по программе «Ресурс». |
| 13. | П.И. Глушко, А.Ю. Журавлев, Н.А. Хованский, Б.М. Широков, А.В. Шиян, Н.А. Семенов. Влияние силицидных покрытий на прочностные и пластические свойства сплава 5ВМЦ. Журнал физики и инженерии поверхности. 2016, т. 1, №2, с. 166 - 169. |
| 14. | С.А. Крохмаль, Т.Н. Зуева, А.А. Сущая. Применение технического продукта «Бархос» в CVD–методе получения карбидохромовых покрытий. Журнал физики и инженерии поверхности. 2016, т. 1, №2, с. 175 - 185. |
| 15. | С.А. Крохмаль, Т.Н. Зуева, А.А. Сущая. Структура и свойства многослойных карбидохромовых покрытий, получаемых методом MOCVD из технического продукта «Бархос». Журнал физики и инженерии поверхности. 2016, т. 1, №2, с. 194 - 206. |
| 16. | А.Ю. Журавлёв, Н.А. Хованский, Д.А. Хижняк, Б.М. Широков, Н.А. Семёнов, А.В. Шиян, С.В. Стригуновский, А.И. Евсюков, А.Б. Шевцов, Е.А. Назаренко, Н.Н. Пилипенко. Получение карбида кремния химическим газофазным, плазмохимическим и сублимационным методами. Вопросы Атомной Науки и Техники. Серия «Физика плазмы». 2017, №1(107), с. 191 - 194. |
| 17. | А.Ю. Журавлёв, А.В. Шиян, Н.А. Семёнов, Б.М. Широков. Разработка процесса газофазного и плазмохимического осаждения покрытия на основе карбида бора. Вопросы атомной науки и техники. Серия «Физика радиационных повреждений и радиационное материаловедение». 2017, №2(108), с. 156 - 159. |
| 18. | О.Ю. Журавльов, О.В. Шиян, М.О. Семенов, Б.М. Широков, С.В. Стригуновський. Осадження карбіду бору газофазним методом. Проблеми корозійно-механічного руйнування, інженерія поверхні, діагностичні системи: матеріали конференції КМН-2017. Львів, 2017, с. 119 - 122. |
| 19. | K.S. Bakai, S.A. Bakai, K.V. Kovtun, V. Gorbatenko. The Effect of Ultrasonic Vibrations on the Mechanical Properties of Nanocrystalline Titanium. Problems of Atomic Science and Technology. Series «Vacuum, Pure Materials, Superconductors». 2018, №1(113), p. 154 - 161. |
| 20. | А.Y. Ghuravlyov, B.M. Shirokov, А.V. Shijan. Gas-phase Deposition of Cavitation-resistant Coatings Based on Boron Carbide. Chemistry, Physics and Technology of Surface. 2018, v. 9, No. 4, p. 368 - 372. |
| 21. | A.N. Deryzemlia, A.I. Yevsiukov, V.I. Radchenko, D.A. Khizhnyak, P.G. Kryshtal, A.Yu. Zhuravlov, A.V. Shijan, S. Strigunovskiy, Yu.A. Pelypets, B.M. Shirokov. Hydrogen Reduction of Silicon Tetrachloride in Low Temperature Non-equilibrium Plasma of a Induction RF discharge. Problems of Atomic Science and Technology. Series «Plasma Physics». 2019, No. 1(119), p. 222 - 224. |
Employees

SHYROKOV BORIS MYKHAYLOVYCH
Head of the Department of “Gas-phase and Plasma Chemical Processes”
Doctor of Technical Sciences in specialty 05.02.01 – Materials Science
Senior Researcher
e-mail: shirokov@kipt.kharkov.ua
Field of scientific interests:
research on the processes of obtaining of multicomponent coatings by gas-phase, plasma-chemical and hybrid methods.

ZHURAVLIOV OLEKSANDR YURIYOVYCH
Head of the Laboratory of “Plasma Chemical Processes”
Candidate of Technical Sciences in Specialty 05.02.01 – Materials Science
e-mail: girik081179@gmail.com
Field of scientific interests:
studying of the processes of gas-phase and plasma-chemical deposition of materials based on Si, SiC, B4C, W, Mo, MoSi2, WSi2, etc.

SAFONOV VOLODYMYR YOSIPOVYCH
Group of gas-phase and plasma chemical deposition of materials
Senior Researcher
Candidate of Technical Sciences in specialty 01.04.07 – Solid State Physics
e-mail: safonov600@gmail.com
Field of scientific interests:
research into vacuum-arc coatings.

KROKHMAL SERHIY OLEKSANDROVYCH
Researcher
Candidate of Technical Sciences in Specialty 01.04.07 – Solid State Physics
e-mail: krokhmal@kipt.kharkov.ua
Field of scientific interests:
high-speed vapor deposition of chromium carbide coatings at low temperatures; protection against corrosive and erosive wear of the surface of products with complex profiles, long channels of small cross-section, capillaries and dead cavities.